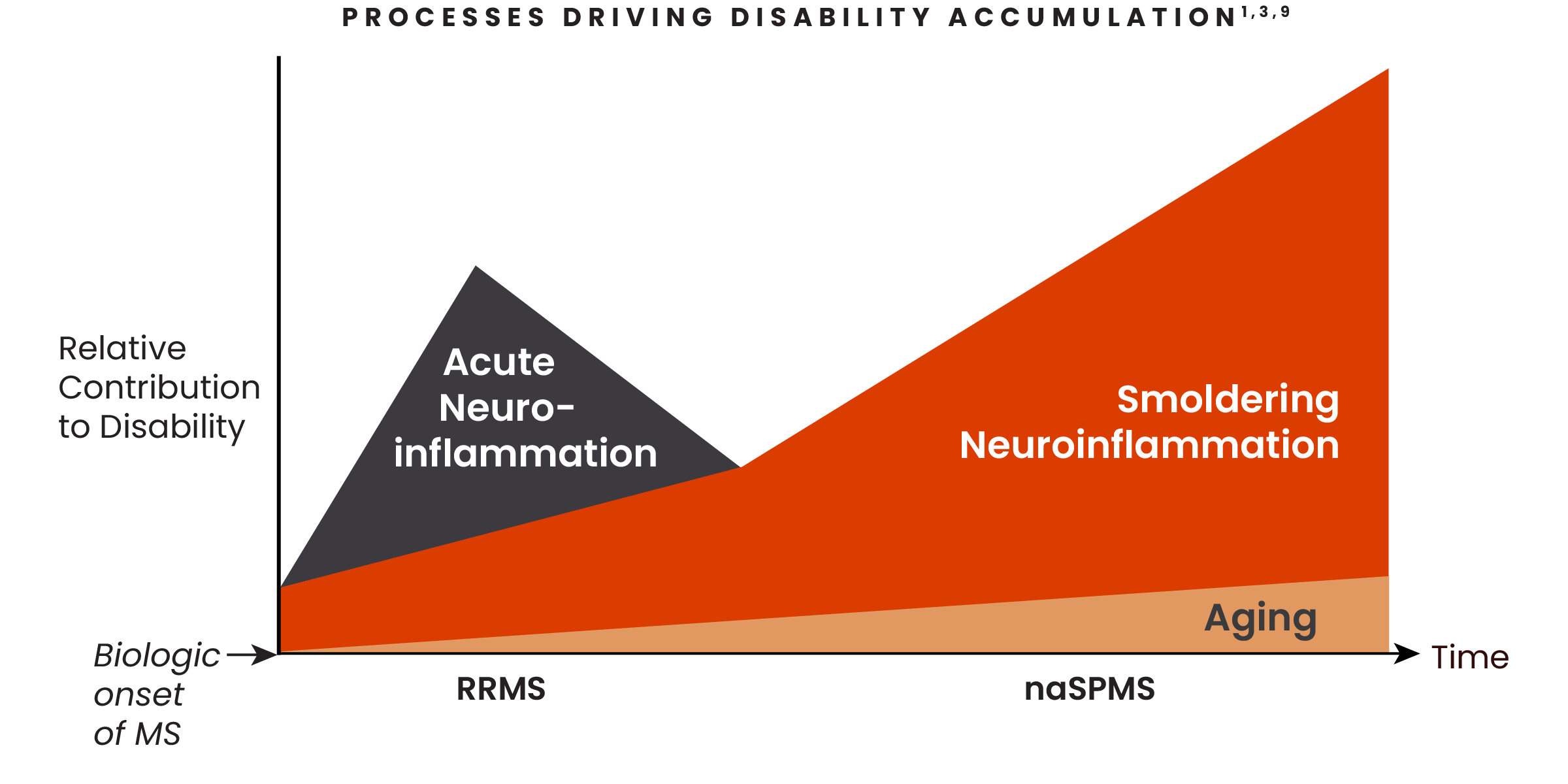
Smoldering neuroinflammation starts at disease onset and increasingly drives disability accumulation1,2
The relative contribution of both acute and smoldering neuroinflammation shifts as patients progress from RRMS to naSPMS.1,3
Biological changes in the prodromal phase of MS and microglial activation in clinically isolated syndrome (CIS)/radiologically isolated syndrome (RIS) demonstrate that smoldering neuroinflammation begins even before the first clinically apparent relapse or acute lesion.1,2,4-8
- Over the course of MS, acute neuroinflammation may decline, but smoldering neuroinflammation persists in the absence of relapses and acute lesions1
- Disability accumulation driven by smoldering neuroinflammation can happen throughout the disease spectrum9
With the increasing contribution of smoldering neuroinflammation to disability accumulation over the course of MS, specific therapeutic approaches that address this process across the disease spectrum from RRMS to naSPMS are required.9
Hear from the experts
Bhupendra O. Khatri, MD, FAAN, discusses the onset of smoldering neuroinflammation at the 2023 AAN Annual Meeting
Smoldering Stories
Smoldering neuroinflammation may drive Albert's disability accumulation—hear his story.
Learn About the Impact
Identify the early physical and cognitive changes of disability accumulation
References:
-
Giovannoni G, Popescu V, Wuerfel J, et al. Smouldering multiple sclerosis: the ‘real MS’. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2022;15:17562864211066751. doi:10.1177/17562864211066751
-
Giovannoni G. The neurodegenerative prodrome in multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol. 2017;16(6):413-414.
-
Filippi M, Amato MP, Centonze D, et al. Early use of high-efficacy disease-modifying therapies makes the difference in people with multiple sclerosis: an expert opinion. J Neurol. 2022;269(10):5382-5394.
-
Absinta M, Lassmann H, Trapp BD. Mechanisms underlying progression in multiple sclerosis. Curr Opin Neurol. 2020;33(3):277-285.
-
Giannetti P, Politis M, Su P, et al. Increased PK11195-PET binding in normal-appearing white matter in clinically isolated syndrome. Brain. 2015;138(1):110-119.
-
Suthiphosuwan S, Sati P, Absinta M, et al. Paramagnetic rim sign in radiologically isolated syndrome. JAMA Neurol. 2020;77(5):653-655. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.0124
-
Bjornevik K, Munger KL, Cortese M, et al. Serum neurofilament light chain levels in patients with presymptomatic multiple sclerosis. JAMA Neurol. 2020;77(1):58-64. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.3238
-
Cortese M, Riise T, Bjørnevik K, et al. Preclinical disease activity in multiple sclerosis: a prospective study of cognitive performance prior to first symptom. Ann Neurol. 2016;80(4):616-624. doi:10.1002/ana.24769
-
Cree BAC, Hollenbach JA, Bove R, et al; University of California, San Francisco MS-Epic Team. Silent progression in disease activity-free relapsing multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 2019;85(5):653-666.